Throat cancer is a serious condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. It’s important to be aware of the signs, symptoms, causes, and available treatments to ensure early detection and effective management. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the details of throat cancer, providing you with the knowledge you need to take proactive steps towards your health.
Understanding Throat Cancer
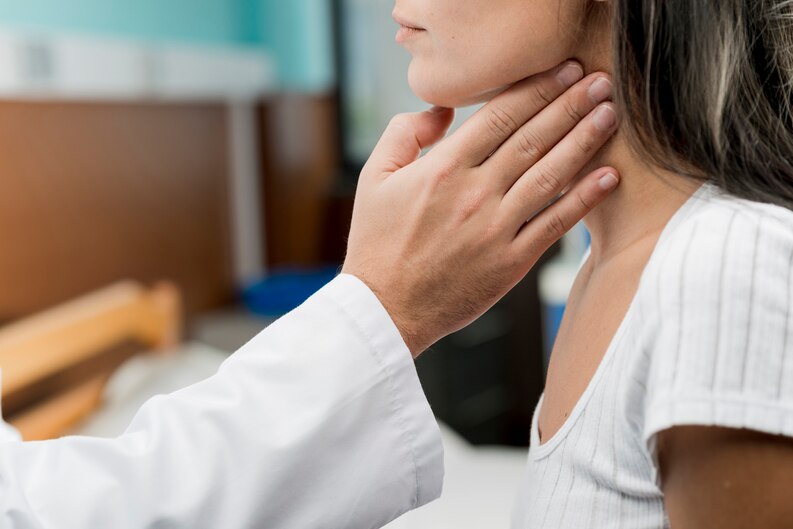
Throat cancer, also known as laryngeal or pharyngeal cancer, refers to the abnormal growth of cells in the throat or voice box. It can occur in various parts of the throat, including the voice box (larynx), the pharynx (the hollow tube that starts behind the nose and ends in the esophagus), and the tonsils.
Common Signs and Symptoms
- Persistent sore throat
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Unexplained weight loss
- Lump or swelling in the neck
- Chronic cough or coughing up blood
- Ear pain
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of throat cancer:
- Tobacco and Alcohol: Heavy and prolonged use of tobacco and alcohol are major risk factors. Smoking and alcohol consumption can irritate the throat lining, increasing the likelihood of cell changes.
- HPV Infection: Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, particularly certain strains, can increase the risk of throat cancers. HPV-related throat cancers are more common in younger individuals.
- Diet: A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables may increase the risk of developing pharyngeal cancer.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Chronic acid reflux can irritate the throat and increase the risk of cancer.
- Occupational Exposure: Exposure to certain chemicals and substances, such as asbestos and wood dust, in certain work environments can elevate the risk.
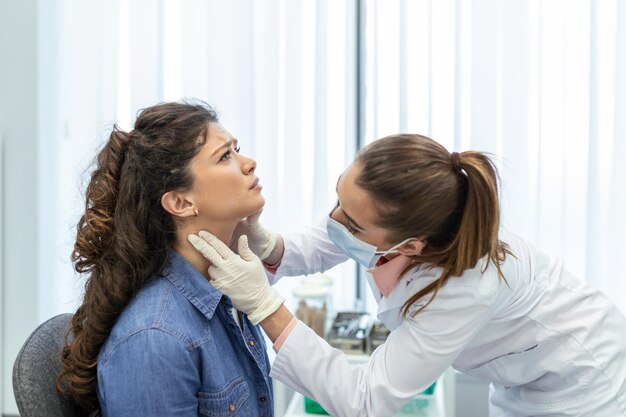
Diagnosing Throat Cancer
If you experience persistent symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a medical professional. Diagnosis often involves:
- Physical Examination: The doctor examines the throat, neck, and mouth for abnormalities.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs provide detailed images of the throat.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample is collected and examined under a microscope to confirm cancer.

Treatment Options
The treatment plan depends on the stage of cancer and overall health. Options may include:
- Surgery: Removing the cancerous tissue, lymph nodes, or part of the voice box.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Administering powerful drugs to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that specifically target cancer cells are used to disrupt their growth.

FAQs
A: While prevention isn’t guaranteed, avoiding tobacco, limiting alcohol, practicing safe sex, and adopting a healthy diet can reduce the risk.
A: Yes, pharyngeal cancer is treatable, especially when detected early. Successful treatment outcomes depend on the stage of cancer and the chosen treatment approach.
A: Yes, non-smokers can develop pharyngeal cancer, particularly due to factors like HPV infection and other risk factors.
A: Treatment side effects vary but may include changes in voice, swallowing difficulties, and fatigue. Rehabilitation and support services can help manage these effects.
A: Offer emotional support, help with appointments and tasks, and encourage healthy habits during and after treatment.
A: The outcome depends on various factors. Early detection and timely treatment improve the chances of cure.
Conclusion
Throat cancer is a complex condition with various causes and risk factors. Recognizing the signs, understanding the causes, and seeking prompt medical attention are crucial for effective treatment and improved outcomes. By staying informed and proactive, you can take control of your health and make informed decisions regarding your well-being.